This document (notebook) describes three ways of making mazes (or labyrinths) using graphs. The first two are based on rectangular grids; the third on a hexagonal grid.
Author Archives: Anton Antonov Antonov
Day 22 – Numerically 2026 Is Unremarkable Yet Happy
This document explores the properties and relationships of the integer 2026. It is classified as a semiprime and a happy number, with 365 serving as one of its primitive roots. While 2026 may not stand out significantly in number theory, it offers a great opportunity to create elaborate visualizations that highlight some interesting aspects of the number.
Day 9 – Monadic programming examples
This document provides examples of monadic pipelines for computational workflows in Raku. It expands on the blog post “Monad Laws in Raku” by including practical, real-life examples.
Day 6 – Robust code generation combining grammars and LLMs
This document (notebook) discusses different combinations of Grammar-Based Parser-Interpreters and Large Language Models to generate executable code from Natural Language Computational Specifications.
Day 2 – Doing Data Science with Raku
This document provides an overview of Raku packages, as well as related documents and presentations, for doing Data Science using Raku. A comprehensive list of references is given.
Day 17 – Chebyshev Polynomials and Fitting Workflows
This post explores the use of Chebyshev polynomials in regression and curve fitting workflows. It highlights various packages that facilitate these processes, providing insights into their features and applications.
Day 12 – Graphs in Raku
This blog post discusses the development of graph theory algorithms in Raku. Moderate number of examples is used.
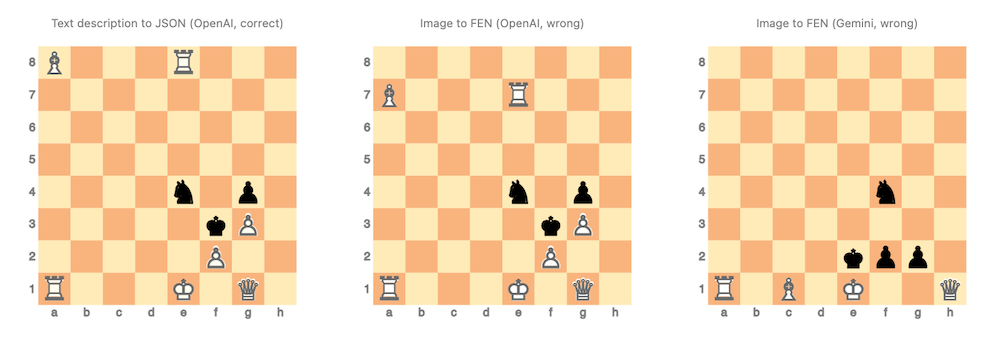
Day 4 – Don’t use Forsyth-Edwards Notation to play chess with LLMs
The article discusses the limitations of using Forsyth-Edwards Notation (FEN) for chess interactions with Large Language Models (LLMs). The document introduces various topics, including creating visual plots of chess positions, and developing an LLM persona called “ChessMaster” for interactive chess play.
Day 24 – Streamlining AI vision workflows
In this document we provide examples of easy to specify computational workflows that utilize Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology for understanding and interpreting visual data. I.e. using “AI vision.”
Day 21 – Using DALL-E models in Raku
In this blog post we proclaim recent creation and updates of several Raku packages that facilitate the utilization of the OpenAI’s DALL-E 3 model.